Using the dataset from the previous insight[1], we will show you how to clean it up before we start the analysis.
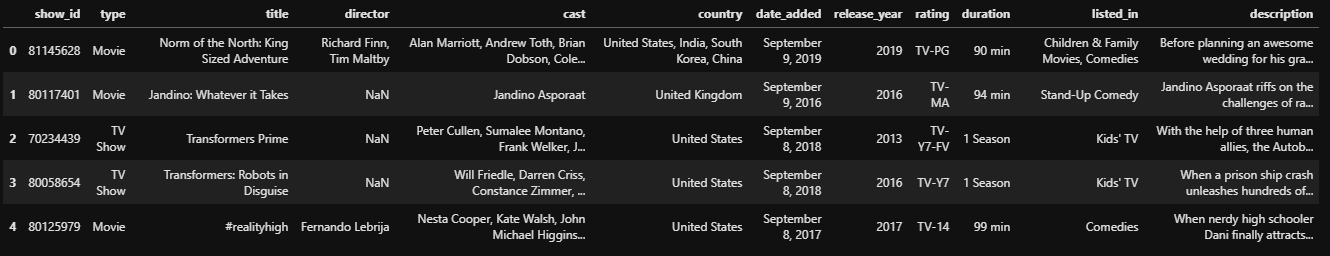
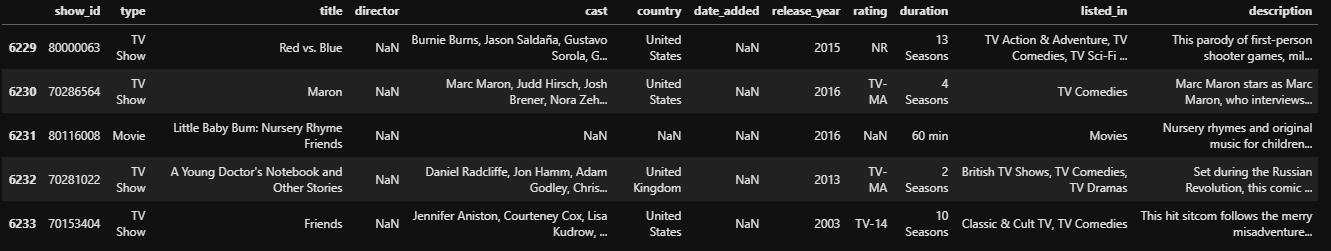
First off, when we import a dataset, we can use the head() or tail() functions to check the top or bottom 5 rows, respectively.
You can also pass a number to head() and tail() to overwrite the default value of 5.
Using importedRawData.head() we get:
Using importedRawData.tail() we get:
This is useful to know right away if your dataset has loaded or not.
As you can see, there are a lot of columns in this dataset.
To check the total number of rows and columns in your dataset, add .shape to your DataFrame.

This dataset has 6234 rows and 12 columns.
Rows start from 0 instead of 1. This is why the last columns show_id is 6233 instead of 6234.
We will remove the columns we don't need for our analysis and leave the ones we will use in this workout.
To determine which columns we will remove, let's first check which cells have missing data.
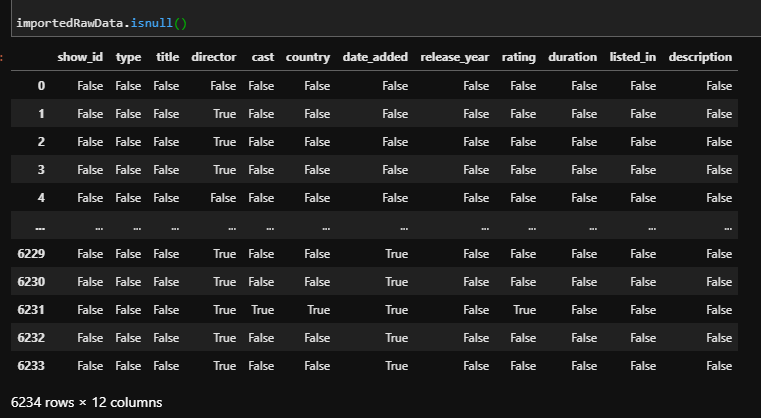
To check which data is missing run the .isnull() command:
This will give us a table with True / False values. True meaning empty.
Footnotes
[1:Previous Dataset]